Steel Glossary
Hardox 450
| C*) | Si*) | Mn*) | P*) | S*) | Cr*) | Ni*) | Mo*) | B*) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-rolled steel | max. | 0.18 | 0.25 | 1.30 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.003 |
| Hot-rolled steel & Quarto-Sheet | max. | 0.26 | 0.70 | 1.60 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 1.40 | 1.50 | 0.60 | 0.005 |
The steel is a fine-grain steel. *) Intended alloying elements
Hardox 450 is a hardened wear-resistant steel used for various applications. It can be formed by bending and can be welded easily.
| Hardness (Guaranteed Value) |
HBW 425-475 (Quarto-Sheet 3.2 - 80.0 mm Thickness) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Impact Toughness (Guaranteed Value) |
Testing Temperature -40°C |
Charpy V-notch Impact Toughness in Longitudinal Direction, minimum 50 J |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yield Strength (Typical Value, not guaranteed) |
Approx. 1,250 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Delivery Condition | Hardened and Tempered | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat Treatment | Hardox 450 is not intended for further heat treatment. The properties cannot be maintained if the steel is exposed to temperatures above 250°C. Note: For applications at higher temperatures up to 590°C, we recommend Toolox 44. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surface | According to EN 10163-2 Class A, Subclass 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
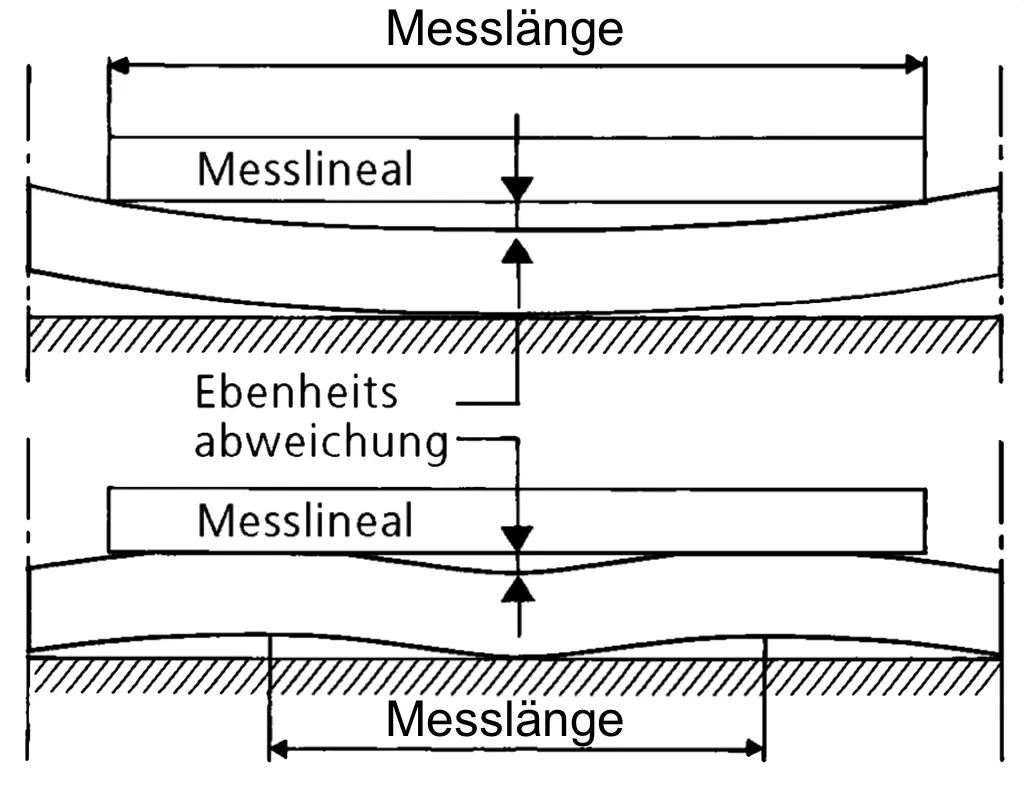
| Flatness |
Tolerances according to Hardox Flatness Guarantee Class D for Quarto-Sheet, stricter than EN 10029. For Hot-rolled Strip according to Hardox Flatness Guarantee Class A, tighter than EN 10051 , and for Cold-rolled Strip according to Hardox Flatness Guarantee Class B.
Flatness is given in millimeters, measured on a 1-meter ruler. Note: Toolox 44 Quarto-Sheet meets stricter flatness requirements for thicknesses of 5.0-7.9 mm = 4 mm/1,000 mm, 8 mm/2,000 mm, and 8.0-99.9 mm = 3 mm/1,000 mm, 6 mm/2,000 mm. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weldability |
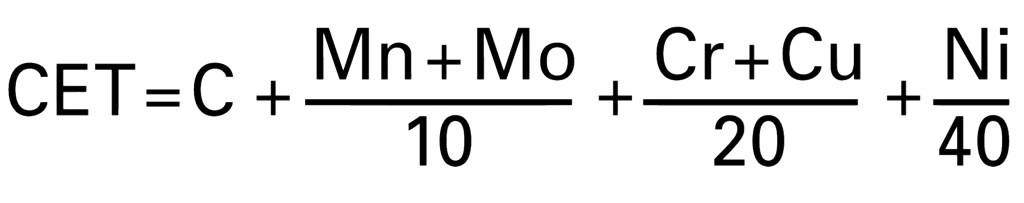 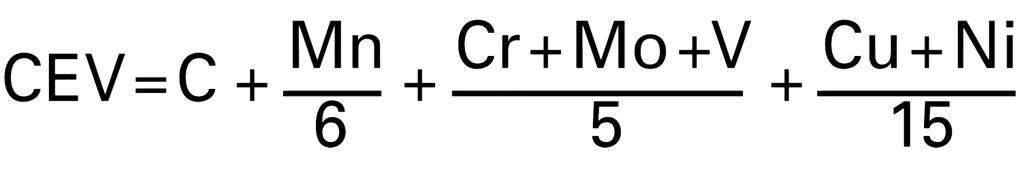 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bending |
The bendability for Quarto-Sheet corresponds to the Hardox bending guarantee Class E. Strip-Metal corresponds to the Hardox bending guarantee Class C for Cold-rolled Strip and Class B for Hot-rolled Strip . The guarantees comply with at least DIN EN 10025-6 and EN ISO 7438. The ratio of bending tool radius to sheet thickness is mentioned.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ultrasonic Testing
Each sheet is thoroughly tested, and 3.1 certificates are available. The internal standards are often stricter than the industry standard.
Surface Inspection1)
| According to EN 10 160 |
Distance between parallel test lines [mm] | Minimum error area to be considered [mm²] | Maximum allowable error area [mm²] | Maximum number of local errors [number/m²] | Corresponding steel-iron delivery conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 100 | 1,000 | 10,000 | 1 | SEL 072 Class 5 |
| S0 | 100 | 1,000 | 5,000 | 20 | - |
| S1 | 100 | 100 | 1,000 | 15 | SEL 072 Class 3 |
| S2 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 10 | SEL 072 Class 2 |
| S3 | 50 | 20 | 50 | 10 | SEL 072 Class 1 |
Edge zone testing2)
| According to EN 10 160 |
Width of Edge Zone2) [mm] | Minimum error length to be considered [mm] | Maximum allowable error length [mm] | Maximum allowable error area [mm²] | Maximum number of errors per m Length | Corresponding steel-iron delivery conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E0 | 50 - 100 | 50 | 100 | 2,000 | 6 | - |
| E1 | 50 - 100 | 25 | 50 | 1,000 | 5 | SEL 072 Class 3 |
| E2 | 50 - 100 | 20 | 40 | 500 | 4 | SEL 072 Class 2 |
| E3 | 50 - 100 | 15 | 30 | 100 | 3 | SEL 072 Class 1 |
| E4 | 50 - 100 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 2 | - |
1) The test can be ordered and conducted as a comprehensive examination, for example, E1S1 or E2S2, or as a test of only the edge zones or surface, for example, E1 or S1.
2) The width of the edge zone in the edge zone inspection varies depending on the thickness of the sheet.
The Thickness Tolerances of the sheets according to AccuRollTech™ are narrower than DIN EN 10 029.
| Nominal Thickness [mm] | Hardox Tolerance Class A [mm] | Maximum Thickness Variation in the Sheet [mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | ||||
| - | 4.9 | -0.3 | +0.4 | 0.5 | |
| 5.0 | - | 7.9 | -0.3 | +0.6 | 0.6 |
| 8.0 | - | 14.9 | -0.4 | +0.6 | 0.7 |
| 15.0 | - | 24.9 | -0.5 | +0.7 | 0.8 |
| 25.0 | - | 39.9 | -0.7 | +0.8 | 1.0 |
| 40.0 | - | 79.9 | -0.9 | +1.5 | 1.1 |
| 80 | - | -1.0 | +2.2 | 1.2 | |
Hardox-Sheets have an amazing flatness.
| 3.2-3.9 | 4.0-4.9 | 5.0-5.9 | 6.0-19.9 | 20.0-130.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardox 450 | Quarto-Sheet Class C Measurement length 1,000mm |
15mm | 7mm | 5mm | 4mm | 3mm |

Hardox sheets come with a standard rust protection coating and individual sheet markings.
Welding Guidelines
Hardox combines unique wear resistance with excellent weldability. All common welding methods can be used for joining Hardox with weldable steels.
For best welding results, pay attention to dryness, cleanliness, and freedom from corrosion. Special attention should be given to the selection of welding materials, temperatures, heat input, and joint geometry.
Low-alloy or unalloyed welding materials with a tensile strength of 500 MPa are suitable for Hardox and Toolox. Hardox 450 in thicknesses of 0.7 – 6.0 mm allows materials with strengths of 900 MPa. Low-alloyed materials result in higher hardness, which promotes wear resistance. If the wear resistance of the weld is crucial, considering the application of a wear protection layer through overlay welding can be beneficial.
| Welding Processes | DIN EN ISO-Classification |
|---|---|
| MAG / Solid wire electrode | EN ISO 14341-A- G 38x EN ISO 14341-A- G 42x |
| MAG / Flux-cored wire electrode | EN ISO 17632-A- T 42xH5 EN ISO 17632-A- T 46xH5 |
| MAG / Metal powder flux-cored wire electrode | EN ISO 17632-A- T 42xH5 EN ISO 17632-A- T 46xH5 |
| MMA / Stick electrode | EN ISO 2560-A E 42xH5 EN ISO 2560-A E 46xH5 |
| UP / Submerged arc welding | EN ISO 14171-A- S 42x EN ISO 14171-A- S 46x |
| TIG / Tungsten inert gas welding | EN ISO 636-A- W 42x EN ISO 636-A- W 46x |
low-alloy or unalloyed fillers
Stainless welding fillers can be used for all Hardox steels, and for Toolox 44, they should be preferred. They allow welding at 5 – 20°C without preheating, except for Hardox 600 and Hardox Extreme. SSAB recommends the following materials, which provide a yield strength of 500 MPa.
| Welding Processes | DIN EN ISO-Classification |
|---|---|
| MAG / Solid wire electrode | EN ISO 14343-A: B 18 8 Mn/ EN ISO 14343-B: SS307 |
| MAG / Flux-cored wire electrode | EN ISO 17633-A: T 18 8 Mn/ EN ISO 17633-B: TS307 |
| MAG / Metal powder flux-cored wire electrode | EN ISO 17633-A: T 18 8 Mn/ EN ISO 17633-B: TS307 |
| MMA / Stick electrode | EN ISO 3581-A: 18 8 Mn/ EN ISO 3581-B: 307 |
| UP / Submerged arc welding | EN ISO 14343-A: B 18 8 Mn/ EN ISO 14343-B: SS307 |
| TIG / Tungsten inert gas welding | EN ISO 14343-A: W 18 8 Mn/ EN ISO 14343-B: SS307 |
austenitic Fillers
When welding Hardox, the same gases are generally used as when welding low-alloy or non-alloy steels.
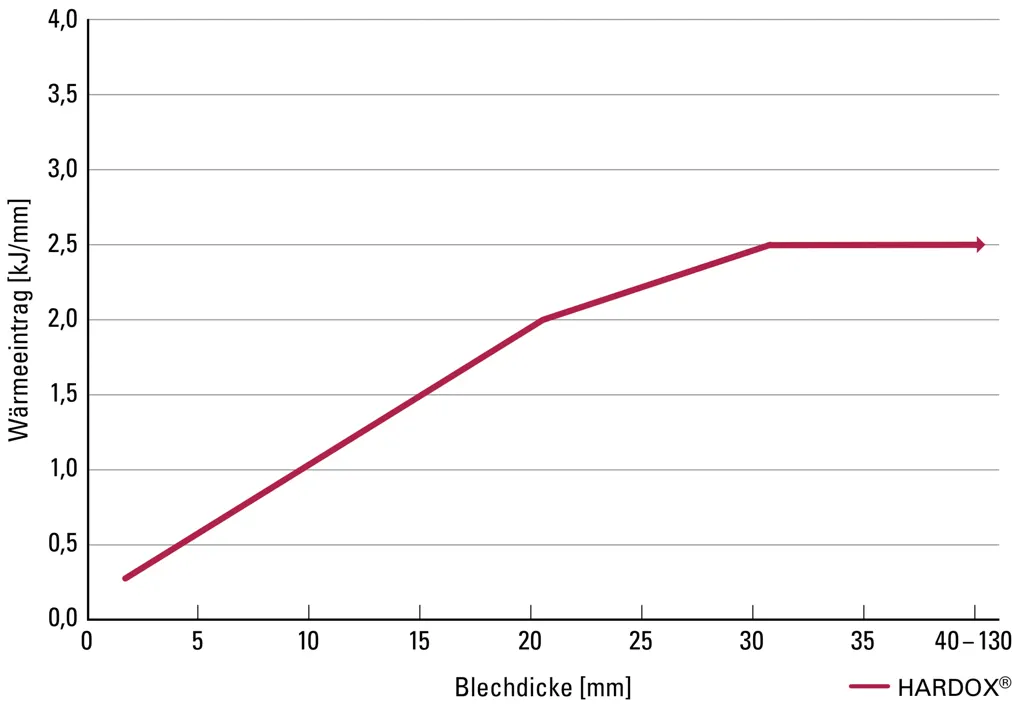
Recommended heat input max.
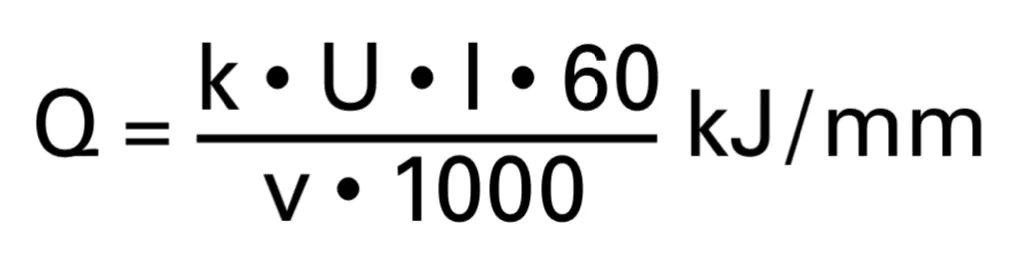
hydrogen content
The danger of hydrogen embrittlement exists in steels. This danger is mitigated by:
- Preheating the welding area
- Measuring the preheat temperature
- Using welding consumables with a maximum of 5ml of water per 100g
- Keeping the welding joint free from rust, grease, oil, and cold
- Applying a suitable welding process
- Avoiding a welding gap over 3mm at the narrowest point of the weld joint
Preheating
Preheating is extremely important for a good weld joint. The recommended preheat temperatures are shown in the following table for low-alloy or unalloyed materials.
Please note:
- For sheets of different thicknesses, use the preheat temperature of the thicker sheet.
- For different sheet materials, use the preheat temperature of the material with the higher value.
- For heat input below 1.7kJ/mm, increase the temperature by 25°C; for heat input below 1.0kJ/mm, please refer to the WearCalc program.
- In low outside temperatures or high humidity, increase the temperature by 25°C.
- For DV or DY joints, start the first bead outside the center of the sheet.
Recommended Minimum Working Temperature
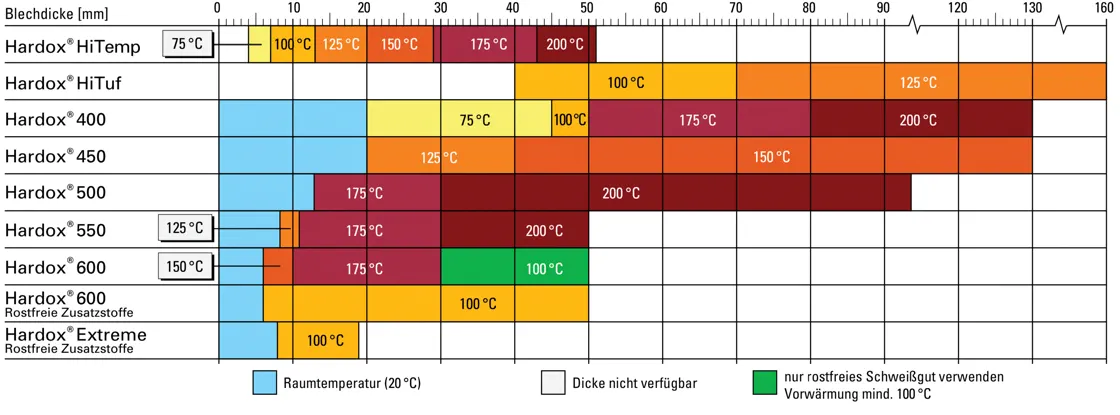
The maximum temperatures after welding one pass and before welding the next pass are:
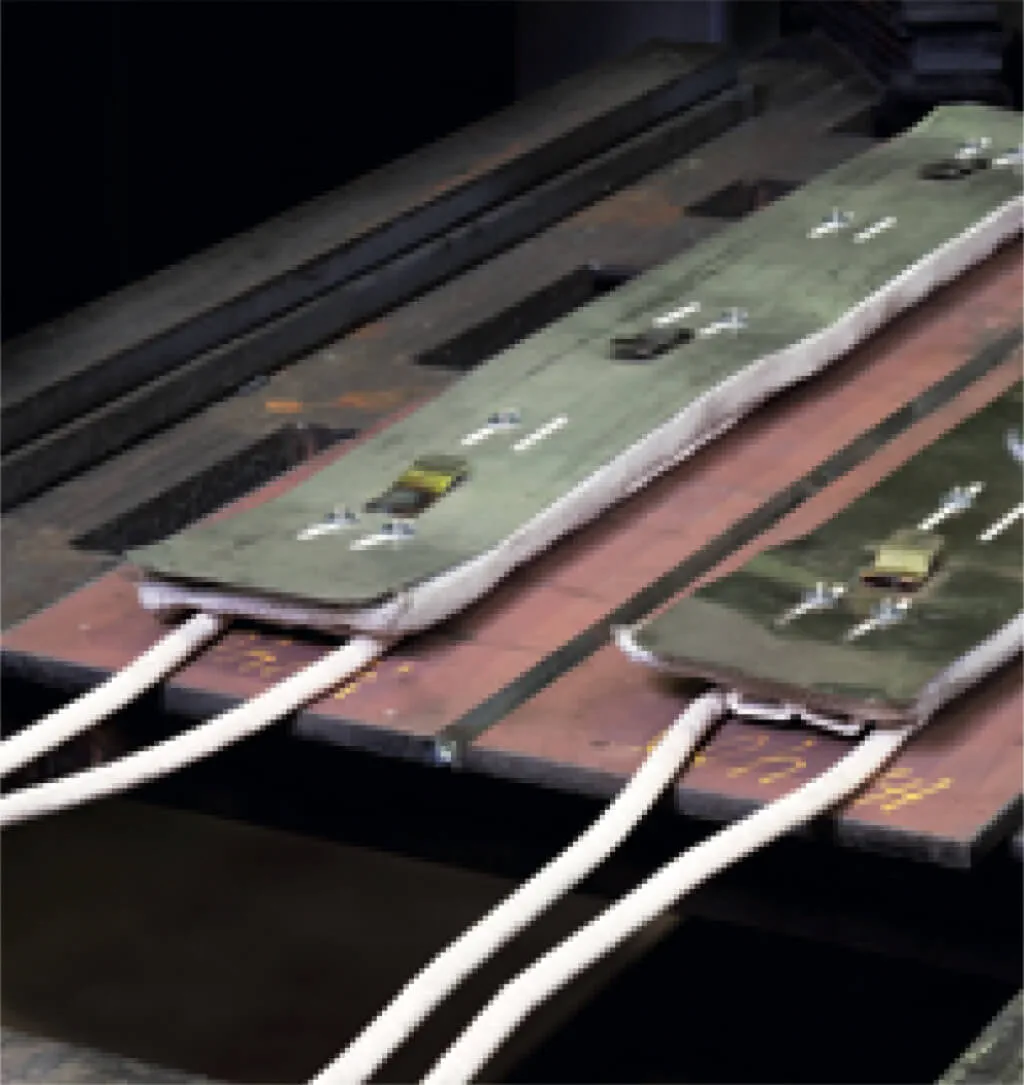
It is practical to measure the temperature on the backside.
It is recommended to wait about 2 minutes per 25mm of plate thickness.
The temperature should be reached approximately 75 - 150mm on both sides of the weld joint.
Primed Sheets
Due to the low zinc content, welding can be done directly on the Hardox primer. However, it is advantageous to remove the primer with a wire brush to avoid porosity. Good ventilation is important for the health of the welder and those nearby.
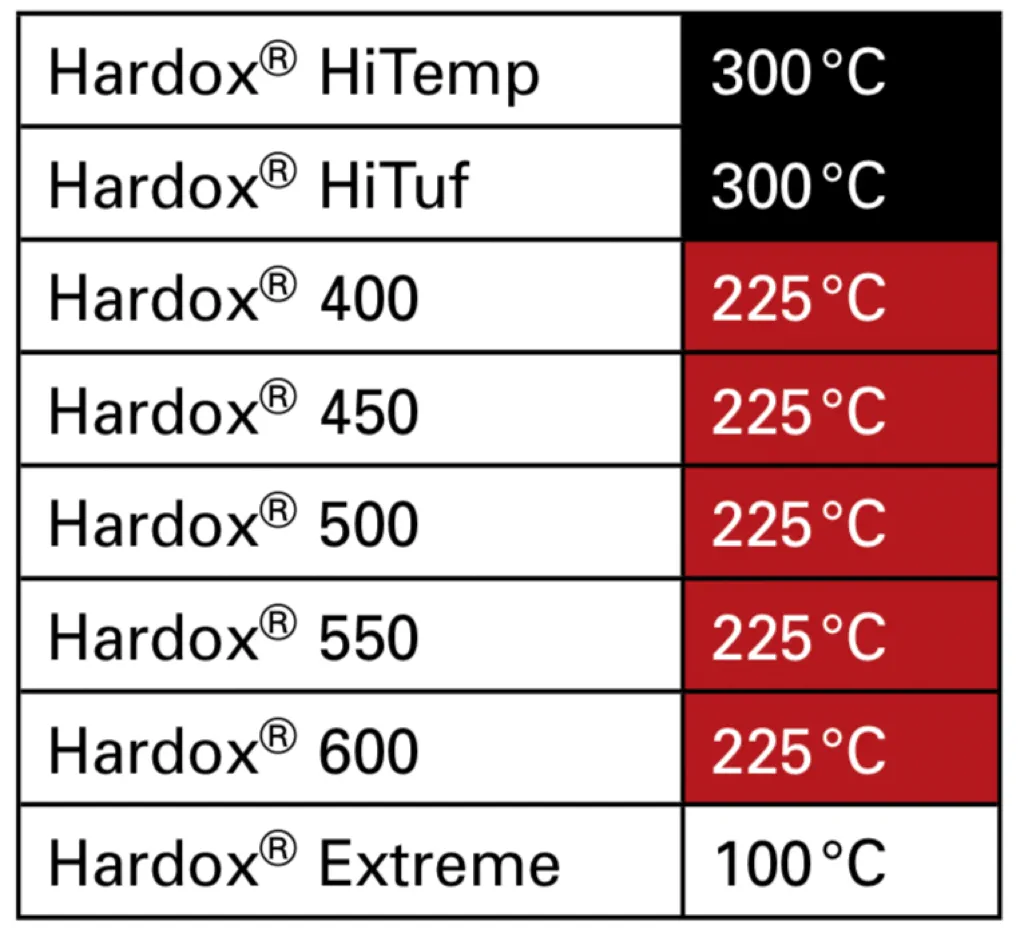
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment after welding is not recommended to preserve the mechanical properties of Hardox.
Hardness Comparison Table for Toolox and Hardox
| Tensile Strength MPa |
715 | 790 | 820 | 861 | 935 | 995 | 1.011 | 1.090 | 1.169 | 1.245 | 1.328 | 1.412 | 1.494 | 1.580 | 1.758 | 1.940 | 2.130 |
| Vickers Hardness HV |
205 | 233 | 243 | 261 | 289 | 311 | 317 | 345 | 373 | 401 | 429 | 458 | 485 | 514 | 569 | 627 | 682 |
| Brinell Hardness HBW |
225 | 250 | 260 | 275 | 300 | 320 | 325 | 350 | 375 | 400 | 425 | 450 | 475 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 650 |
| Rockwell Hardness HRC |
19 | 22.5 | 24 | 26 | 29 | 32 | 32.5 | 35.5 | 38 | 40 | 42.5 | 44.5 | 46.5 | 49 | 52.5 | 55 | 57.5 |
Attention please!
Some features of our webshop are not supported by your current browser version.
We recommend updating your browser or using a different browser.

